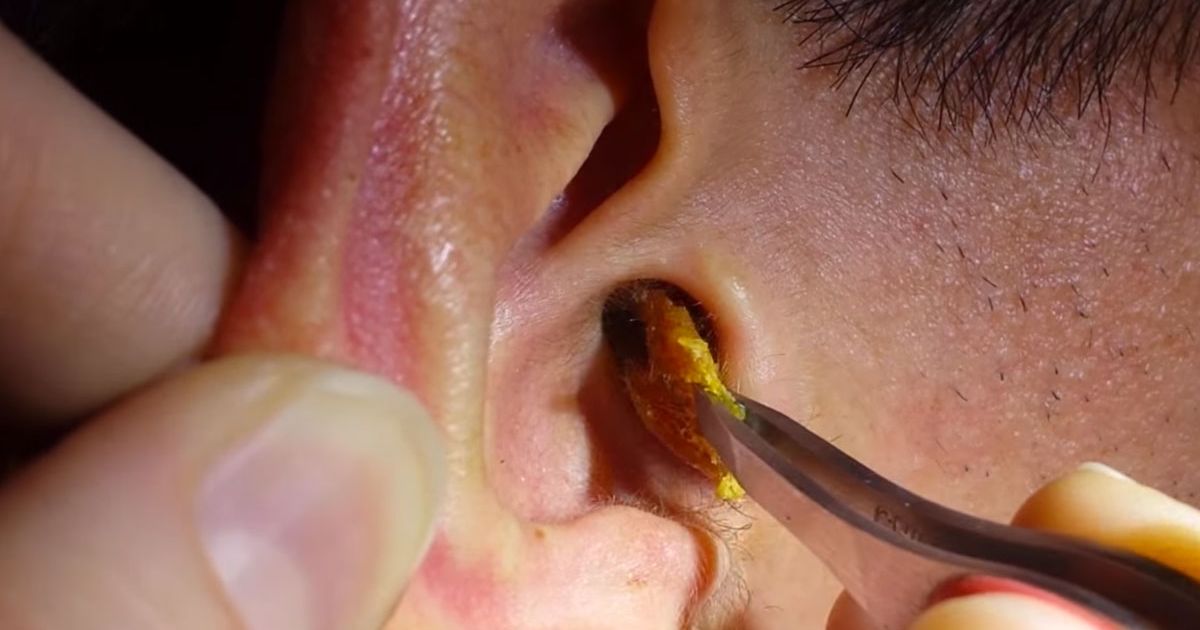
Ear Wax
Earwax is a lubricating and antimicrobial protective fluid secreted by the ear. It is called cerumen in medical terms.The ear is quite capable of cleaning itself through a ‘conveyor-belt’ like process in which the ear canal skin grows from inside out and it is aided by chewing and other jaw movements in pushing out the older earwax.
Earwax Causes
Blockage, or impaction, also occurs when the wax gets pushed deep within the ear canal. Earwax blockage is one of the most common ear problems doctors see.
- The most common cause of impactions is the use of Q-tips and other objects such as bobby pins and rolled napkin corners, which can remove superficial wax but also pushes the rest of the wax deeper into the ear canal.
- Hearing aid and earplug users are also more prone to earwax blockage.
Earwax Treatment and Self-Care at Home
- Over-the-counter wax softening drops such as Debrox or Murine may be put into the affected ear and then allowed to drain out after about five minutes while holding the head to the side, allowing the drops to settle. Sitting up again will let the drops drain out by themselves.
- A bulb-type syringe may be used to gently flush the ear with warm water. The water should be at body temperature to help prevent dizziness.
- Ear candling is not recommended.