Adenoidectomy
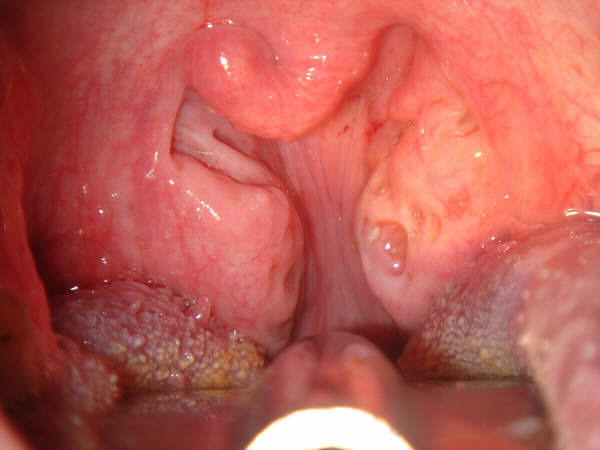
Adenoids are a mass of tissue that, along with your tonsils, help keep you healthy by trapping harmful germs that pass through the nose or mouth. Your adenoids also produce antibodies to help your body fight infections. Unlike tonsils, which can be easily seen by opening your mouth, you cannot see the adenoids. A doctor has to use a small mirror or special instrument with a light to see the adenoids. Sometimes X-rays may be taken to see them more clearly.
While adenoids play an important role in keeping a person healthy, as you get older, adenoids become less important, because your body is able to fight infection in other ways. In fact, adenoids often get smaller around age 5 or 6 and virtually disappear by the teen years.
What Happens During an Adenoidectomy?
An adenoidectomy is performed by a doctor who specializes in ear, nose, and throat surgery. It occurs in a hospital or outpatient surgical center under general anesthesia meaning your child is put to sleep. The tonsils and adenoids can be removed through the mouth so no additional incisions are made except for where the tissues are removed.
Most patients can go home following the procedure; but, you should expect to be in the surgical center for around four or five hours after the surgery so that your child can be carefully monitored. Your doctor can give you more specific instructions as to what to expect based on your child’s particular health needs.
Recovery From Adenoidectomy
After surgery, your child may feel nauseous until the anesthesia completely wears off. In the week following the adenoidectomy, your child may experience the following:
- Sore throat: Your child’s throat may be sore for seven to ten days following the procedure and eating can be uncomfortable.
- Fever: Your child may have a low fever several days after the surgery. If the fever gets higher than 102 F, call the doctor. Seek medical attention if fever is accompanied by other symptoms such as lethargy, nausea, vomiting, headache or stiff neck.
- Mouth breathing: Mouth breathing and snoring may occur following the surgery, due to swelling in the throat. Breathing should return to normal once swelling goes down, usually 10 to 14 days after surgery. Seek medical attention if there is difficulty breathing.
- Pain: Some throat and ear pain is normal for a few weeks following surgery. The doctor should prescribe medicine to help control pain.
- Scabs in the mouth: Thick white scabs will develop where the tonsils and adenoids were removed. This is normal and most scabs fall off in small pieces within 10 days after surgery. Do not let your child pick at the scabs. These scabs may also cause bad breath.