Voice change (Hoarseness)
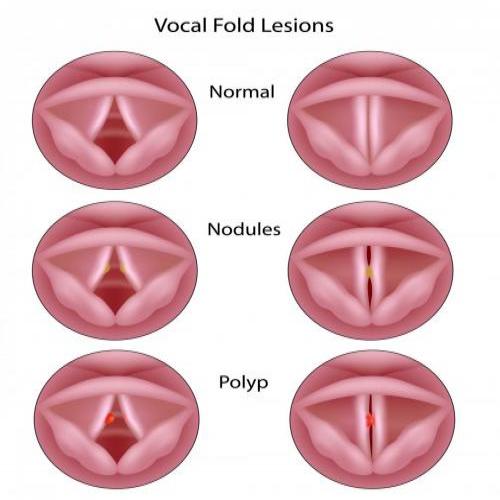
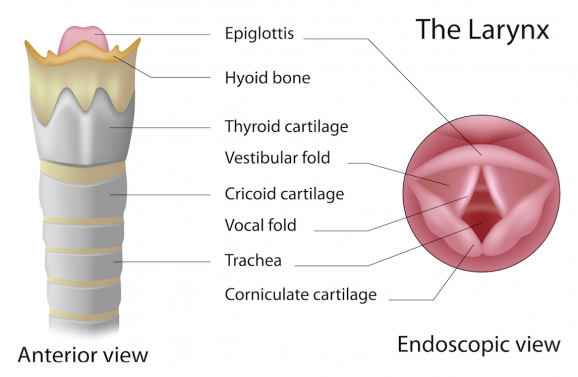
Abnormal changes in the voice are called hoarseness. When hoarse, the voice may sound breathy, raspy, strained, or show changes in volume or pitch (depending on how high or low the voice is). Voice changes are related to disorders in the sound-producing parts (vocal folds) of the voice box (larynx). While breathing, the vocal folds remain apart. When speaking or singing, they come together and, as air leaves the lungs, they vibrate, producing sound. Swelling or lumps on the vocal folds hinder vibration, altering voice quality, volume, and pitch.
What Are The Causes Of Hoarseness ?
Hoarseness is generally caused by irritation of, or injury to, the vocal cords. The larynx (also referred to as the voice box), is the portion of the respiratory (breathing) tract containing the vocal cords. The cartilaginous outer wall of the larynx is commonly referred to as the “Adams apple.” The vocal cords are two bands of muscle that form a “V” inside the larynx. When we sing or speak, the vocal cords vibrate and produce sound.
How can hoarseness be prevented?
- If you smoke, quit.
- Avoid agents which dehydrate the body, such as alcohol and caffeine.
- Avoid “second hand” (passive) smoke.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Humidify your home.
- Watch your diet – avoid spicy foods and alcohol.
- Try not to use your voice too long or too loudly.
- Seek professional help if your voice is injured or hoarse.